How to Become an Investment Banker
Curious about how to become an investment banker? Read about the intricacies of a typical investment banking career roadmap—access free job market insights on key skills, qualifications, and salaries. Explore top career paths and identify the most in-demand skills and qualities in the industry.
Join over 2 million professionals who advanced their finance careers with 365. Learn from instructors who have worked at Morgan Stanley, HSBC, PwC, and Coca-Cola and master accounting, financial analysis, investment banking, financial modeling, and more.
Start for FreeUnderstanding how to become an investment banker goes beyond gaining experience and pursuing continuous education. It’s about building a strong network and staying updated with industry trends.
Investment bankers usually start their careers as analysts at investment banks. With experience and further education, they can advance to senior analyst or vice president roles, where they oversee and mentor juniors in the field.
What is the investment banking job outlook? According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the field is expected to rise by 7% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations. This growth translates to approximately 40,100 job openings each year, largely due to the need to replace workers who leave the occupation. But what skillset do you need to become an investment banker?
Our recent study of 1,000 investment banking jobs posted on Indeed examines the trends, experience, expertise, qualifications, and salaries for these roles in 2024, offering a practical perspective on how to become an investment banker.
Key Highlights
- Role Overview: Investment bankers link companies with investors and facilitate capital flow.
- Investment Banking Job Outlook: The investment banking sector is expected to grow by 7% from 2022 to 2032.
- Investment Banking Career Paths: Core duties include underwriting, M&A, financial advisory, and market making.
- Investment Banker Education Requirements: Essential degrees include finance, business, economics, with advanced degrees (MBA) and certifications (CFA, CPA) being highly beneficial.
- Key Investment Banking Skills: Necessary skills include financial modeling, financial analysis, communication, and client management.
- Top Investment Banks: Leading firms with job openings are JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley, Goldman Sachs, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation, and Jefferies & Company Inc.
- Investment Banking Salaries: Common salary ranges from $160,000 to $200,000, with entry-level roles offering $80,000 to $100,000.
- Job Type: 75.4% of positions are full-time, with limited remote work opportunities (3.5%).
Table of Contents
- Investment Banking Job Description
- How to Become an Investment Banker: Education, Skills, Certificates, and Experience
- How to Become an Investment Banker: Employment and Hiring Firms
- Breaking Into Investment Banking: Jobs and Salaries
- How to Become an Investment Banker: Steps
- Investment Banking Job Outlook in 2024
- FAQs
Investment Banking Job Description
Investment bankers are finance professionals who help companies, governments, and other entities raise capital. They act as intermediaries between organizations that need funding and investors who are willing to provide it, ensuring that capital flows efficiently through the economy. An investment banking job description typically covers the following aspects, depending on the seniority level and scope.
Bonus Resource: Get our FREE Investment Banking Course Notes and kickstart your career in the field.
Underwriting New Securities
Investment bankers underwrite new debt and equity securities for all types of corporations. This involves assessing the value and risk of the securities, pricing them correctly and then selling them to investors. Becoming an investment banker requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and investor behavior, as companies look to raise funds through initial public offerings (IPOs) or other financial instruments.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
An investment banker might specialize in facilitating mergers and acquisitions. They provide strategic advice to companies considering merging with or acquiring another business, ensuring that the transactions are financially sound and beneficial. Excelling in this area is often a milestone in any investment banking career path, as it includes performing due diligence, negotiating terms, and structuring the deal.
Financial Advisory Services
Investment bankers may offer strategic financial advice on a range of issues, including capital structure, business valuations, and market strategies. This advisory role is a critical component of the investment banking career path, helping companies make informed decisions that align with their long-term goals and market conditions.
Market Making
Many investment bankers engage in market making, which involves buying and selling securities to provide liquidity to the markets. By doing so, they help stabilize the market and ensure that there is always a buyer or seller available for securities transactions.
Risk Management
Managing financial risks is another sought-after expertise in the investment banking job market. Investment bankers analyze potential risks associated with financial transactions and advise clients on how to mitigate these. This includes hedging strategies and derivative instruments to protect against market volatility.
Raising Capital
Jobs in investment banking go beyond underwriting—investment bankers assist companies in raising capital through other means, such as private placements and bond offerings. They tailor capital-raising strategies to the specific needs of their clients, whether it’s through equity, debt, or hybrid instruments.
Research and Analysis
Conducting in-depth market research and financial analysis is essential for providing accurate and timely advice. They are the foundation of an investment banking career path, equipping professionals with the knowledge required to analyze market trends, economic indicators, and financial statements to inform their recommendations and strategies.
How to Become an Investment Banker: Education, Skills, Certificates, and Experience
Here’s an overview of the typical investment banker profile, based on our analysis of 1,000 job postings on Indeed USA.
1. Education: What Degree Do You Need for Investment Banking?
What degree do you need for investment banking? A business or banking degree is typically required for the majority of positions. This includes degrees in finance, economics, business administration, or a related field.
2. Investment Banking Technical Skills
- Financial Modeling and Analysis: Proficiency in financial modeling is highly sought after. This involves the ability to create complex financial models to support investment decisions, forecasting, and valuation tasks.
- Data Analysis Tools: Familiarity with data analysis tools and ERP systems is preferable, and proficiency in common financial software is implied.
- Microsoft Office: How to break into investment banking always begins with upskilling in Excel. Experience in other Microsoft Office tools such as Word, Access, PowerPoint, and Outlook is also important.
3. Investment Banking Soft Skills
- Communication Skills: Around 69% of the investment banking jobs posted on the hiring platform emphasize the necessity of strong communication skills. This includes verbal and written communication abilities, essential for client interactions, presentations, and report writing.
- Analytical Skills: Strong analytical skills to assess and interpret complex financial data are almost equally necessary.
- Detail-Oriented: A meticulous approach to work, with a keen eye for detail, is critical to ensure accuracy in financial modeling and reporting.
4. Role-Specific Skills
- Technical Aptitude: Comfort with using and understanding advanced financial software and investment banking tools, though AI tools like ChatGPT were not specifically required.
- Client Management: An investment banker must build and maintain strong relationships with clients, demonstrating exceptional interpersonal skills.
- Geographic Mobility: Willingness to work in major financial hubs, with New York leading in investment banking jobs (21.1% of the total postings).
5. Credentials: Investment Banking Certificate
Breaking into investment banking can be easier when you have a finance certificate. Although specific credentials were not detailed in the summary, possessing relevant financial testaments such as—Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Series 7, and Series 63 licenses—can be beneficial and are often required or preferred by employers.
6. Experience and Industry Knowledge
- Work Experience: While 77.9% of investment banking jobs we analyzed don’t specify the required experience, having relevant practical insights in investment banking, financial analysis, or a related field is typically advantageous.
- Industry Knowledge: Most investment banking job descriptions emphasize an in-depth understanding of financial markets, investment strategies, and industry regulations.
- General Profile: Investment bankers are expected to have a solid educational foundation in finance or related fields, excellent technical and analytical skills, strong communication abilities, and relevant professional experience.
How to Become an Investment Banker: Employment and Hiring Firms
Employment Type
Most investment banking job descriptions indicate full-time commitment, making up 75.4% of the listings. This indicates a strong industry preference for employees who can commit to long-term, continuous roles—reflecting the high demands and expectations within the field of investment banking. This further emphasizes the importance of rigorous on-site investment banking training.
Contract roles are rare, constituting just 0.6% of the job listings. Similarly, seasonal, permanent, part-time, apprenticeship, internship, and temporary positions each account for less than 0.5% of the total. This proves the sector’s reliance on extensively trained full-time professionals over temporary or flexible job arrangements.
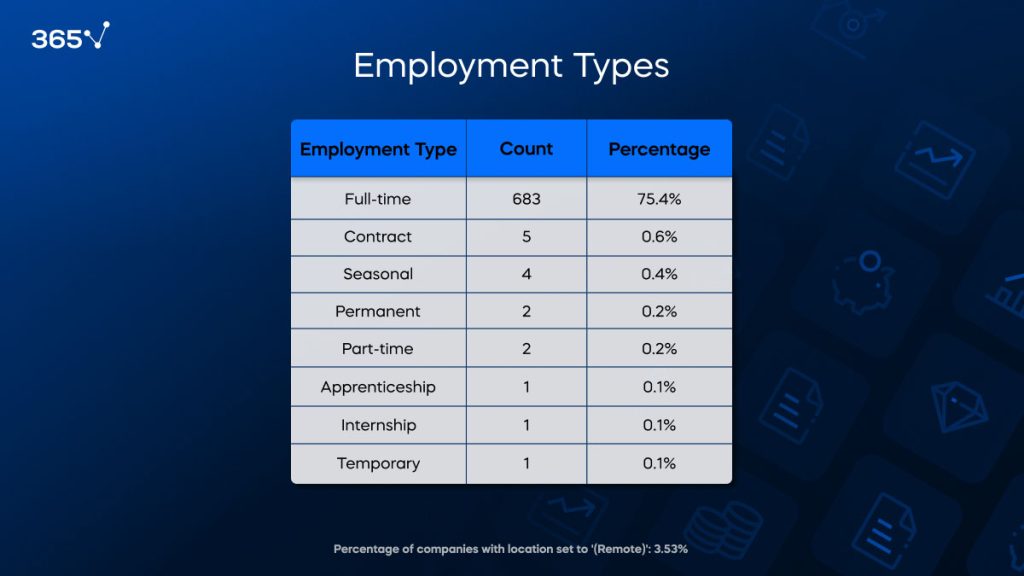
Remote work opportunities are scarce, with only 3.53% of roles offering this option. Despite a global shift towards flexible working conditions, investment banking careers remain predominantly office-based. This is likely due to the need for close teamwork, secure data handling, and real-time decision-making.
Top Investment Banks
Our analysis supports the idea that a few major players dominate the investment banking job market in the US. JPMorgan Chase & Co. is a standout, responsible for 24.8% of all job postings. This underscores the firm’s extensive reach and leadership in the financial industry.
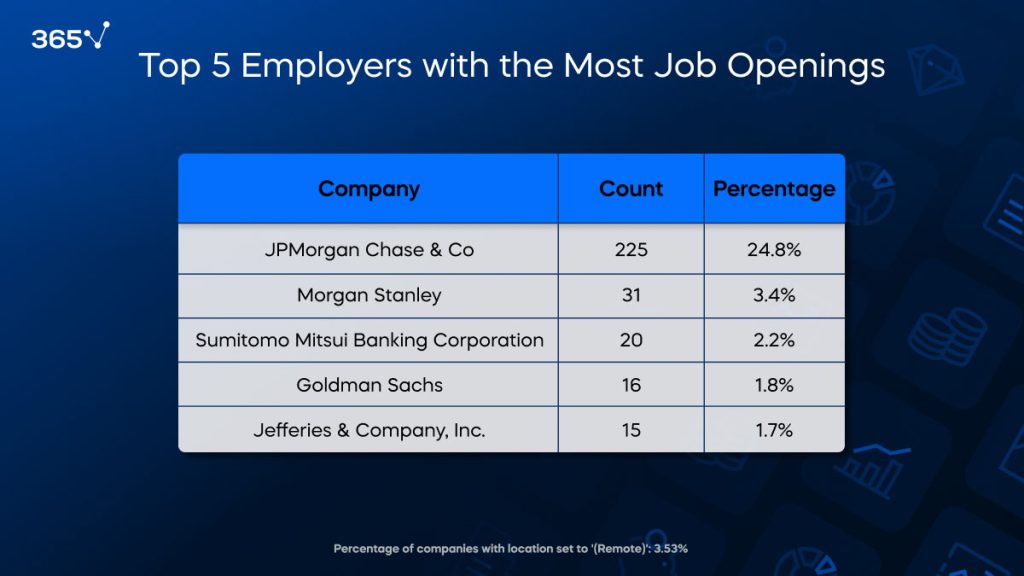
Other significant employers include Morgan Stanley (3.4%), Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (2.2%), Goldman Sachs (1.8%), and Jefferies & Company Inc. (1.7%). These institutions are well-regarded for their powerful investment banking operations and substantial roles in the global financial landscape.
The heavy concentration of investment banking jobs from these top companies implies that established financial institutions are the primary sources of employment in investment banking. This trend highlights their dominance in shaping the investment banking job market outlook.
Breaking Into Investment Banking: Jobs and Salaries
Investment bankers wear many hats—functioning as advisors, intermediaries, and analysts. Their expertise in financial markets and strong analytical and negotiation skills make them indispensable in tackling complex financial transactions and helping clients achieve their financial and strategic goals.
Here’s a breakdown of the areas you can focus on when breaking into investment banking.
1. Advisory Services
Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
Buy-Side Advisory: Assisting clients in finding acquisition targets, conducting due diligence, valuing the target, and negotiating the terms of the acquisition, a crucial aspect of an investment banking career.
Sell-Side Advisory: Helping companies looking to sell their business by identifying potential buyers, preparing marketing materials, conducting valuations, and managing the sale process.
Corporate Restructuring
Advising companies on reorganizing their structure to improve profitability or address financial difficulties. This may include—debt restructuring, asset sales, and other strategic moves—essential for anyone looking to understand how to become an investment banker.
2. Capital Raising
Equity Capital Markets (ECM)
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs): Assisting private companies in going public by underwriting the sale of shares, pricing the offering, and managing the distribution of shares—highlighting investment banking job growth opportunities.
Follow-On Offerings: Helping public companies raise additional capital by issuing more shares.
Private Placements: Raising capital through the sale of equity to a select group of investors rather than the public market.
Debt Capital Markets (DCM)
Bond Issuances: Assisting clients in raising funds by issuing bonds, including—structuring the bond, setting terms, and finding investors.
Loan Syndications: Arranging large loans that are too big for a single lender to handle, involving multiple financial institutions. The increasing complexity of these arrangements positively influences an investment banker’s job outlook.
3. Underwriting
Risk Assessment: Evaluating the risks associated with issuing securities, including market conditions and the financial health of the issuer. Effective risk assessment is key to a favorable investment banker’s job outlook.
Pricing: Determining the appropriate price for new securities offerings to balance the interests of the issuer and investors.
Distribution: Ensuring that securities are sold to a broad range of investors, often through a network of sales and trading desks.
4. Trading & Brokerage
Market Making: Investment banking careers often involve buying and selling securities to provide liquidity to the markets, ensuring that clients can buy or sell investments.
Proprietary Trading: Investing the firm’s capital to profit from market movements.
Brokerage Services: Investment banking jobs also facilitate transactions for clients in various financial markets, including—equities, bonds, commodities, and derivatives.
5. Research & Analysis
Equity Research: Providing detailed analysis and recommendations on individual stocks to help clients make informed investment decisions. Having strong investment banking technical skills further enhances the research process.
Credit Research: Evaluating the creditworthiness of bond issuers and providing insights on fixed-income investments. Both areas are fundamental for a positive investment banker job outlook.
Market Research: Analyzing broader market trends and economic conditions to guide investment strategies and corporate decisions—crucial skills to highlight in your investment banking resume.
6. Compliance and Risk Management
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that all activities comply with relevant financial regulations and laws.
Risk Management: Using specialized investment banking tools, one must assess and mitigate financial risks associated with various transactions and investments.
7. Client Relationships Management
Client Engagement: Investment banking soft skills extend to building and maintaining strong relationships with clients to understand their needs and provide tailored financial solutions.
Deal Execution: Managing the end-to-end process of transactions, an investment banker must ensure that all parties are aligned and that the deal progresses smoothly.
8. Strategic Consulting
Strategic Planning: Breaking into investment banking entails a long-term commitment to clients in developing their strategies for growth, including—market entry, expansion, and diversification.
Valuation Services: Providing accurate valuations of businesses and assets to support various financial transactions and strategic decisions—further highlighting the importance of the investment banking career.
9. Financial Modeling and Analysis
Building Financial Models: Creating detailed financial models to forecast financial performance, evaluate opportunities, and support decision-making—all significant enough to have an impact on the investment banking roadmap.
Scenario Analysis: Analyzing under various scenarios to assess potential outcomes and risks.
Bonus Resource: Watch our YouTube video, “How to Become an Investment Banker”.
Investment Banking Salaries (2024)
Our review of 906 investment banking jobs on Indeed USA highlights a wide spectrum of salary ranges, indicating the variety of roles and levels of experience within the field. Although over 50% of the listings did not disclose specific salary information, we still managed to gather valuable insights from those who did.
Our findings support the common belief of lucrative investment banking salaries, with the majority of firms offering between $100,000 and $200,000.
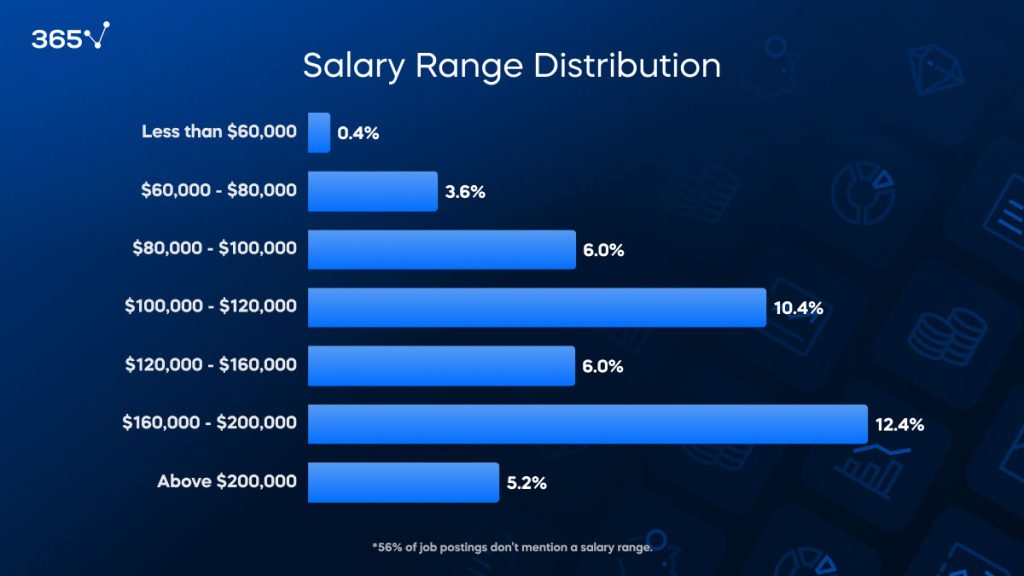
The most common investment banker salary range is $160,000 to $200,000—appearing in 12.4% of the postings. This indicates that numerous positions come with substantial pay, likely reflecting the significant demands, responsibilities, and bonuses associated with these roles. According to Glassdoor, the average salary for investment bankers in the US in 2024 is around $172,531, which corroborates our findings.
Investment banking salaries ranging from $100,000 to $120,000 are also commonly listed, accounting for 10.4% of job postings. These amounts usually pertain to mid-level roles where professionals have gained substantial expertise and manage important financial tasks.
Salaries within the $120,000 to $160,000 range appear in 6% of job postings, typically for seasoned professionals with advanced skills and a proven track record in successful deals and financial strategies. Similarly, investment banking salaries between $80,000 and $100,000 also represent 6.0% of postings—indicating entry-level or early-career positions that still offer competitive pay.
Investment banking salaries over $200,000 are noted in 5.2% of the listings. These roles are typically senior or specialized positions that demand extensive experience and a demonstrated ability to generate substantial revenue.
Only 3.6% of listings indicated salaries between $60,000 and $80,000—showing limited opportunities at the lower end of the pay spectrum. Even less common are roles offering under $60,000 investment banking salaries annually, which make up only 0.4% of postings, underscoring the generally lucrative nature of careers in investment banking.
How to Become an Investment Banker: Steps
- Education: An investor banker career path typically involves obtaining a relevant degree in Business, Finance, Economics, or a related field. Advanced degrees like an MBA can significantly enhance your prospects.
- Technical Skills: Develop strong financial modeling skills, valuation, and data analysis. Proficiency in tools like Excel and financial software such as Bloomberg and PitchBook is essential.
- Certifications: While not always mandatory in investment banking, certifications such as CFA, CPA, and CA are highly valued and can distinguish you in the competitive job market.
- Investment Banking Resume: Prepare a stunning investment banking resume, using our guide to ensure you don’t miss to include the most important skills and competencies employers look for.
- Experience: Gain relevant expertise through internships and entry-level positions. Aim for investment banking careers that offer exposure to financial analysis, mergers and acquisitions, and client advisory services.
- Networking: Build a robust professional network. Attend industry events, join relevant associations, and seek mentorship from seasoned professionals in the field.
- Job Search: Focus your job hunt on major financial hubs and prominent financial institutions. Tailor your investment banking resume and cover letter to highlight your skills, experience, and educational background.
Investment Banking Job Outlook
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts a 7% employment growth for securities, commodities, and financial services sales agents from 2022 to 2032, surpassing the average for all occupations. This growth will result in about 40,100 investment banking jobs annually, mainly due to retirements and career shifts.
Our study of 906 job postings shows promising investment banking salaries, with most roles offering between $160,000 and $200,000. Entry-level positions typically range from $80,000 to $100,000, while experienced professionals can earn much more.
AI and investment banking are still at an early stage in their integration, with many firms stating their investment banker education requirements and interpersonal skills as key prerequisites for employment. Top employers for investment banking careers are JPMorgan Chase & Co., Morgan Stanley, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation, Goldman Sachs, and Jefferies & Company Inc.
New York leads as the primary location for these careers, followed by California and Texas. Only 3.5% of jobs offer remote work, highlighting a preference for office-based roles. Overall, the investment banking job growth in the next decade provides lucrative opportunities for skilled professionals.
Now that you’re aware of the investment banking job outlook, are you ready to learn how to become an investment banker?
Sign up for our Investment Banking Career Track—earn a verifiable 365 Financial Analyst Certificate of Achievement for completing our comprehensive training and passing a rigorous finance exam.
FAQs
Becoming an investment banker typically takes around 4-6 years. This includes earning a bachelor’s degree (4 years) and gaining relevant work experience or internships (1-2 years).
To become an investment banker, you need a bachelor’s degree in finance, business, economics, or a related field. Additionally, strong analytical skills, proficiency in financial modeling, and excellent communication abilities are essential.
Yes, getting into investment banking can be challenging due to its competitive nature. It requires strong academic credentials, relevant internships, networking, and sometimes advanced degrees or certifications.
A degree in finance, business administration, economics, or a related field is best for investment banking. Advanced degrees like an MBA can also enhance your prospects.
