Financial Intermediaries
Join over 2 million professionals who advanced their finance careers with 365. Learn from instructors who have worked at Morgan Stanley, HSBC, PwC, and Coca-Cola and master accounting, financial analysis, investment banking, financial modeling, and more.
Start for Free
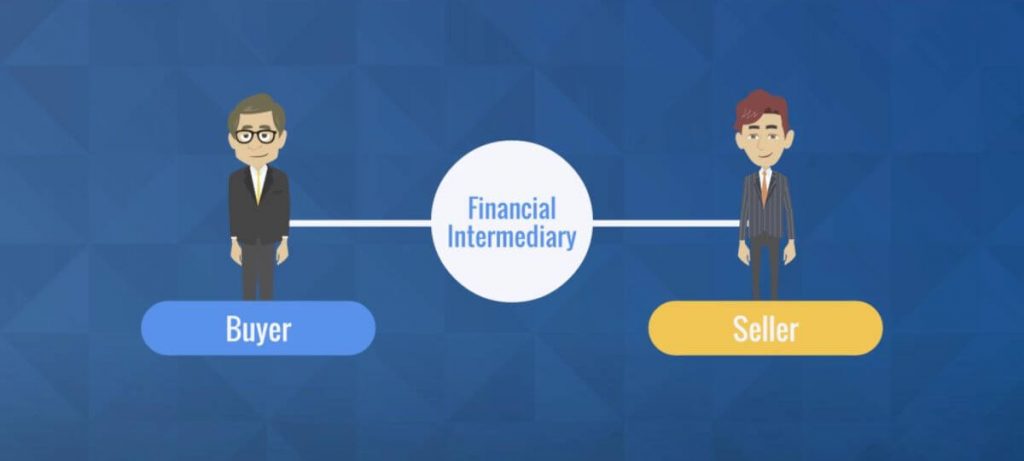
Financial intermediaries act as the middlemen between buyers and sellers to help them achieve their financial goals.
Types of Financial Intermediaries
Intermediaries are vital for a well-functioning financial system and allow their clients to solve the problems they face more efficiently than they could by themselves.
We find seven types of financial intermediaries:
- Brokers, Exchanges, and Alternative trading systems
- Dealers and Securitizers
- Depository Institutions
- Insurance Companies
- Arbitrageurs, and
- Clearinghouses and Custodians
Functions of Financial Intermediaries
The role of financial intermediaries depends on the type of institution. For instance, both dealers and custodians perform important, yet different functions in serving sellers and buyers. In the world of finance, intermediaries generally have three functions – storing assets, transferring funds, and investing.
Storing assets: People who look for a place to store their money or assets can go to a designated financial institution, such as a commercial bank. In turn, the bank is expected to ensure the safety of the assets. Depositors and authorized parties will have access to their funds via checks, deposit slips, or credit cards issued. Besides, bank depositors will receive information about outstanding balances, withdrawals, and any other movements on their accounts.
Transferring funds: Providing loans is the most important function of intermediaries. They transfer money from those who have it to the ones that need finances. This is a win-win situation for all parties involved. On the one hand, the borrower receives the sought-after financing and pays interest to the intermediaries. On the other hand, the lender risks their money by giving it to the borrower and receives a portion of that interest. The remaining amount goes to the intermediaries for ensuring a smooth transaction.
Investing: Financial intermediaries may assist clients in growing their funds. These institutions hire finance professionals to manage clients’ money by trading on various markets to make a profit. In the end, both parties get rewarded for that. Sometimes, these organizations specialize in financial advisory services and charge clients for helping them achieve their financial goals.
Benefits of Financial Intermediaries
Financial intermediaries have many advantages. Three of the most essential ones are:
Spread of Risk: They reduce the investment risk by allowing lenders to spread their assets to a multitude of borrowers. What’s more, they help lenders do a background check on borrowers, which further decreases the risk of default.
Economies of Scale: Financial intermediaries have a great number of clients. That allows them to spread their costs among various parties, thus they require lower service fees.
Diversity of Products: These institutions offer a wide range of services. As a result, it is easier for a borrower and lender to tailor their products and services at a reasonable cost.
Examples of Financial Intermediaries
Some of the most prominent financial intermediaries are:
- Commercial and investment banks
- Insurance companies
- Credit unions
- Pension funds
- Mutual funds
- Investment trusts
Beyond Financial Intermediaries
Financial intermediaries are all around us. They facilitate our day-to-day financial transactions and goals. As such, their impact on the world economic arena is, by all means, undeniable.
Once we know what each of the seven intermediaries does, we will be able to better understand how the financial system functions as a whole.
You may now want to find out more about the first financial intermediary ― Brokers, Exchanges, and Alternative trading systems.
