Need an all-in-one list with the Financial Reporting and Analysis formulas included in the CFA® Level 1 Exam? We have compiled them for you here. The relevant formulas have been organized and presented by chapter. In this section, we will cover the following topics — Basics of Accounting, Income Statements, Balance Sheets, Cash Flow Statements, Financial Analysis Techniques, Inventories, Income Taxes, Current and Non-current Liabilities and Assets.
1. Basics of Accounting
Basic Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Net income
Net~Income = Revenue-Expenses
Gross profit (income)
Gross~profit~(income) = Revenue-Cost~of~goods~sold
Operating profit (income)
Operating~profit~(income) = Profit~before~interest~and~tax~(PBIT) = Gross~profit-Operating~expenses
Profit Before Tax (PBT)
Profit~before~tax~(PBT) = PBIT-Interest~expense
Net profit (income)
Net~profit~(income) = PBT-Tax~expense= Operating~profit-Interest~Expense-Tax~expense
2. Understanding Income Statements
Basic Earnings per Share (EPS)
Basic~EPS= \frac {Net~Income - Preferred~Dividends}{Weighted~average~number~of~common~shares~outstanding}Diluted Earnings per Share (DEPS)
Diluted~EPS= \frac {Adjusted~income~available~for~common~shares}{Weighted~average~common~ and~potential~common~shares~outstanding}Diluted~EPS = \frac {\big[Net~Income-Preferred~dividends\big]+ \big[Convertible~preferred~dividends\big]+ \big[Convertible~debt~interest\big]\big(1-t\big)}{\big(Weighted~average~shares\big)+\big(Shares~from~conv.~pfd.~shares\big)+\big(Shares~from~conversion~of.~conv.~debt\big)+\big(Shares~issuable~from~stock~options\big)}Gross profit margin
Gross~profit~margin = \frac {Gross~profit}{Revenue}Net profit margin
Net~profit~margin = \frac {Net~profit}{Revenue}3. Understanding Balance Sheets
Liquidity Ratios
Current ratio
Current~ratio=\frac {Current~assets}{Current~liabilities}Quick ratio
Quick~ratio=\frac {Cash + Short–term~marketable~securities + Receivables}{Current~liabilities}Cash ratio
Cash~ratio=\frac {Cash + Short–term~marketable~securities}{Current~liabilities}Solvency Ratios
Long-term debt-to-equity
Long–term~debt–to–equity = \frac {Long–term~debt}{Total~equity}Total debt-to-equity
Total~debt–to–equity = \frac {Total~debt}{Total~equity}Debt ratio
Debt~ratio= \frac {Total~debt}{Total~assets}Financial leverage
Financial~leverage = \frac {Total~assets}{Total~equity}Free Cash Flow Measures
FCFF = CFO + [Int × (1 - tax~rate)] - FCInv
CFO = Cash flow from operations
Int = Cash interest paid
FCInv = Fixed capital investment (net capital expenditures)
FCFF = NI + NCC + [Int × (1 – tax~rate)] - FCInv - WCInv
NI = Net income
NCC = Non-cash charges (depreciation and amortization)
Int = Cash interest paid
FCInv = Fixed capital investment (net capital expenditures)
WCInv = Working capital investment
FCFE = CFO - FCInv + Net~borrowing
CFO = Cash flow from operations
FCInv = Fixed capital investment (net capital expenditures)
Net~borrowing = Debt issued – debt repaid
Cash Flow Ratios
Performance Ratios
Cash flow-to-revenue
Cash~flow–to–revenue = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Revenue}Cash-to-income
Cash–to–income = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Operating~income}Cash return-on-assets
Cash~return–on–assets = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Average~total~assets}Cash return-on-equity
Cash~return–on–equity= \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Average~total~equity}Cash flow per share
Cash~flow~per~share = \frac {CFO - Preferred~dividends}{Weighted~average~number~of~common~shares}4. Understanding Cash Flow Statements
Cash Flow Ratios
Coverage Ratios
Debt Coverage
Debt~coverage = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Total~debt}Interest Coverage
Interest~coverage = \frac {CFO + Interest~paid + Taxes~paid}{Interest~paid}Reinvestment ratio
Reinvestment~ratio = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Cash~paid~to~acquire~long–term~assets}Debt payment
Debt~payment = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Cash~paid~to~repay~long–term~debt}Dividend payment
Dividend~payment = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Dividends~paid}Investing and financing ratio
Investing~and~financing~ratio = \frac {Cash~flow~from~operations}{Cash~outflows~from~investing~and~financing~activities}5. Financial Analysis Techniques
Activity Ratios
Receivables~turnover = \frac {Annual~sales}{Average~receivables}Meaning: The efficiency of a company in collecting its trade receivables
Days~of~sales~outstanding = \frac {365}{Receivables~turnover}Meaning: The average number of days a company takes to collect its receivables from clients
Inventory~turnover = \frac {Cost~of~goods~sold}{Average~inventory}Meaning: The efficiency of a company in terms of inventory management
Days~of~inventory~on~hand = \frac {365}{Inventory~turnover}Meaning: The average inventory processing period
Payables~turnover = \frac {Purchases}{Average~trade~payables}Meaning: The efficiency of a company in allowing trade credit to suppliers
Number~of~days~of~payables = \frac {365}{Payables~turnover~ratio}Meaning: The average number of days a company takes to pay its suppliers
Fixed~assets~turnover = \frac {Revenue}{Average~net~fixed~assets}Meaning: The efficiency of a firm in utilizing its fixed assets
Working~capital~turnover = \frac {Revenue}{Average~working~capital}Meaning: The efficiency of a firm in managing its working capital (current assets – current liabilities)
Total~assets~turnover = \frac {Revenue}{Average~total~assets}Meaning: The efficiency of a firm in using its total assets to create revenue
Cash~conversion~cycle = Days~of~sales~outstanding + Days~of~inventory~on~hand - Number~of~days~of~payables
Meaning: The number of days a company takes to convert its investments in inventory and other resources into cash flows from sales
Equity~turnover = \frac {Revenue}{Average~total~equity}Meaning: The efficiency of a firm in utilizing equity to create revenue
Liquidity Ratios
Current~ratio = \frac {Current~assets}{Current~liabilities}Meaning: Ability to meet current liabilities (with total current assets)
Quick~ratio = \frac {Cash + Marketable~securities + Receivables}{Current~liabilities}Meaning: Ability to meet current liabilities (with total current assets, excluding inventory)
Cash~ratio = \frac {Cash + Marketable~securities}{Current~liabilities}Meaning: Ability to meet current liabilities (with cash and marketable securities only)
Defensive~interval = \frac {Cash + Marketable~securities + Receivables}{Average~daily~expenditure}Meaning: The number of days a company can cover its average daily expenses with the use of current liquid assets only
Solvency Ratios
Debt–to–equity = \frac {Total~debt}{Total~shareholder’s~equity}Meaning: Debt as a percentage of total equity
Debt–to–capital= \frac {Total~debt}{Total~debt + Total~shareholder’s~equity}Meaning: Debt as a percentage of total capital
Debt–to–assets= \frac {Total~debt}{Total~assets}Meaning: Debt as a percentage of total assets
Financial~leverage = \frac {Average~total~assets}{Average~total~equity}Meaning: An indicator of a company’s debt financing usage
Interest~coverage = \frac {Earnings~before~interest~and~taxes}{Interest~payments}Meaning: The ability to cover interest expenses
Fixed~charge~coverage = \frac {Earnings~before~interest~and~taxes + Lease~payments}{Interest~payments + Lease~payments}Meaning: The ability to cover interest and lease expenses
Profitability Ratios
Gross~profit~margin = \frac {Gross~profit}{Revenue}Meaning: Gross profitability as a percentage of total revenue
Operating~profit~margin = \frac {Operating~income~(EBIT)}{Revenue}Meaning: Operating profitability (before interest and tax) as a percentage of total revenue
Pre–tax~margin = \frac {EBT}{Revenue}Meaning: Operating profitability (before tax) as a percentage of total revenue
Net~profit~margin = \frac {Net~income}{Revenue}Meaning: Net profitability as a percentage of total revenue
Return~on~assets~(ROA) = \frac {Net~income}{Average~total~assets}Meaning: Net profitability (excluding interest and taxes) as a percentage of total invested funds
Operating~return~on~assets~(ROA) = \frac {Operating~profit~(EBIT)}{Average~total~assets}Meaning: Net profitability (including interest and taxes) as a percentage of total invested funds
Return~on~total~capital = \frac {Operating~profit~(EBIT)}{Average~total~capital}Meaning: Operating profitability as a percentage of total capital
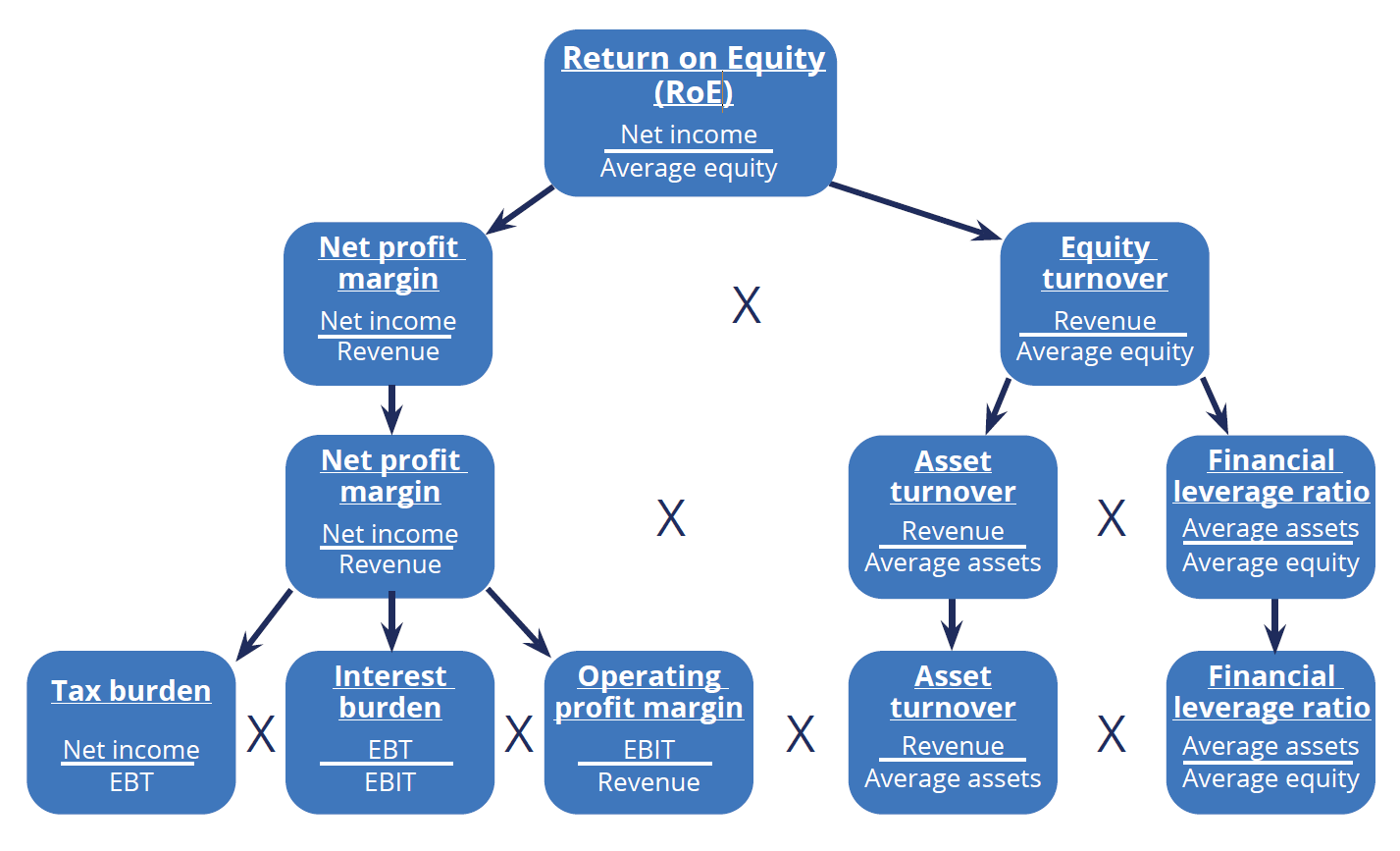
Return~on~equity~(RoE) = \frac {Net~income}{Average~equity}Meaning: Net profitability as a percentage of total equity
Valuation Ratios
Earnings~per~Share~(EPS) = \frac {Net~Income - Preferred~dividends}{Outstanding~number~of~common~shares}Meaning: Income earned per 1 common share outstanding
Price~earnings~(P/E)~ratio = \frac {Share~price}{Earnings~per~share~(EPS)}Meaning: The price that investors are willing to pay per $1 of earnings
P/E~ratio~(company~wide) = \frac {Market~capitalization}{Net~income}Meaning: Total price that investors are willing to pay for a company’s Net income
Dividend~yield = \frac {Dividend~per~share}{Current~share~price}Meaning: The “portion “of a share price that is distributed as dividends
Retention~rate~(RR) = \frac {Net~income - Dividends~declared}{Net~income}Meaning: The “portion” of Net income that is reinvested in the company
Dividend~payout = \frac {Dividends~declared}{Net~income}Meaning: The “portion” of Net income that is distributed as dividends
Sustainable~growth~rate~(g) =RR \times ROE
Meaning: Equity growth rate
DuPont Analysis
Inventories
Where:
FIFO = First-in, First-out method
LIFO = Last-in, First-out method
Ending~inventory = Beginning~inventory + Purchases - Cost~of~goods~sold~(COGS)
Cost~of~goods~sold~(COGS) = Beginning~inventory + Purchases - Ending~inventory
FIFO~inventory = LIFO~inventory + LIFO~reserve
Delta~Cash = LIFO~reserve \times Tax~rate
Delta~Cash = Excess cash saved on the valuation method
FIFO~retained~earnings = LIFO~retained~earnings + LIFO~Reserve \times (1 - Tax~rate)
FIFO~COGS = LIFO~COGS - (Ending~LIFO~reserve - Beginning~LIFO~reserve)
Long-Lived Assets
Straight–line~depreciation~expense = \frac {Cost-Salvage~(residual)~value}{Useful~life}Double–declining~balance (DDB)~depreciation~expense=\frac {2 \times (Cost - Accumulated~depreciation)}{Useful~life}Double-declining balance (DDB) depreciation expense = Double the straight-line depreciation rate
Units~of~production~depreciation~expense= \frac {Cost - Salvage~value}{Life~in~output~units} \times Output~units~in~the~periodEnding~PPE~net~book~value = (Original)~Cost - Accumulated~depreciation
Average~age = \frac {Accumulated~depreciation}{Annual~depreciation~expense}Total~useful~life = \frac {Historical~cost}{Annual~depreciation~expense}Remaining~useful~life = \frac {Ending~PPE~net~book~value}{Annual~depreciation~expense}Income Taxes
Income~tax~expense = Taxes~Payable + Δ~Deferred~Tax~Liabilities~(DTL) - Δ~Deferred~Tax~Assets~(DTA)
Effective~tax~rate = \frac {Income~tax~expense}{Pre–tax~income}Non-Current Liabilities
Interest~expense = Market~rate~at~Issuance \times Balance~sheet~value~of~the~liability~at~the~beginning~of~the~period
Coupon~interest~payment = Coupon~rate~(as~per~contract) \times Par~Value
Follow the links to find more formulas on Quantitative Methods, Economics, Corporate Finance, Alternative Investments, Portfolio Management, Equity Investments, Fixed-Income Investments, and Derivatives, included in the CFA® Level 1 Exam.

