Fundamentals of Financial Reporting
Gain the knowledge and skills necessary to read, analyze, and interpret financial statements with confidence
 Start for free
Start for free
What you get:
- 7 hours of content
- 127 Interactive exercises
- 14 Downloadable resources
- World-class instructor
- Closed captions
- Q&A support
- Future course updates
- Course exam
- Certificate of achievement
Fundamentals of Financial Reporting
 Start for free
Start for free
What you get:
- 7 hours of content
- 127 Interactive exercises
- 14 Downloadable resources
- World-class instructor
- Closed captions
- Q&A support
- Future course updates
- Course exam
- Certificate of achievement
 Start for free
Start for free
What you get:
- 7 hours of content
- 127 Interactive exercises
- 14 Downloadable resources
- World-class instructor
- Closed captions
- Q&A support
- Future course updates
- Course exam
- Certificate of achievement
What you learn
- Gain a thorough understanding of financial statements and develop the ability to quickly identify key financial performance indicators
- Appreciate the importance of financial reporting standards and the quality of published financial information
- Explore key financial reporting standards such as the IASB Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting
- Master the interpretation of profitability measures at different levels of the Income Statement to assess what drove a company’s performance
- Prepare cash flow statements independently using the direct and indirect method
- Perform common-size analysis, interpret accounting warning signs, and recognize fraud motivations
Top Choice of Leading Companies Worldwide
Industry leaders and professionals globally rely on this top-rated course to enhance their skills.
Course Description
Learn for Free

1.1 What does the course cover
3 min

2.1 Introduction to Financial Reporting
4 min
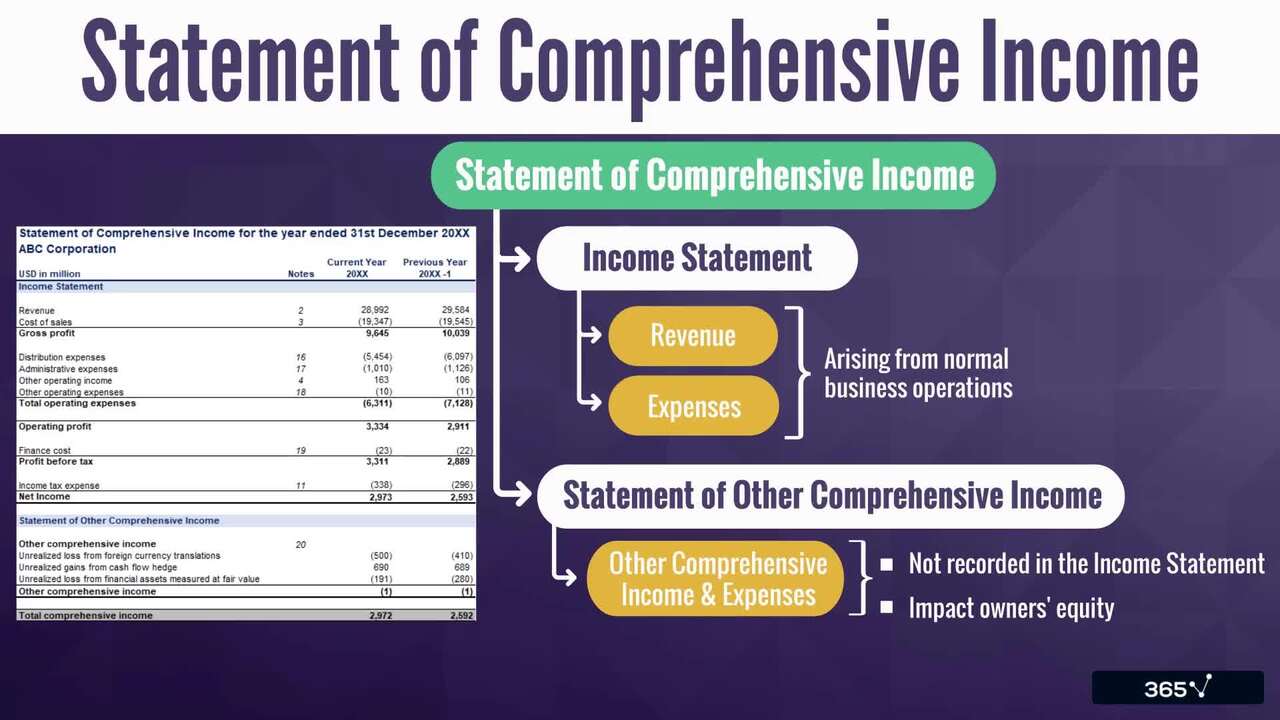
2.2 The Main Financial Statements
9 min

2.3 Supplementary Sources of Financial Information
6 min

2.4 Auditor's Reports
4 min

2.6 Financial Statement Analysis
4 min
Curriculum
- 2. Introduction to Financial Statements Analysis and Financial Reporting13 Lessons 73 MinIn this section, we introduce the main financial statements and supplementary sources of information used in financial analysis. Next, we explain why auditors provide an opinion on published financial information and what the main types of audit reports are. Last but not least, we discuss the importance of setting financial reporting standards and examine the elements of the IASB Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting.Introduction to Financial Reporting4 minThe Main Financial Statements9 minSupplementary Sources of Financial Information6 minAuditor's Reports4 minFinancial Statement Analysis4 minThe Financial Statement Analysis Framework2 minThe Importance of Financial Reporting Standards4 minStandard-setting Bodies and Regulators5 minThe Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting (Part 1)8 minThe Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting (Part 2)8 minBasics of Accounting9 minGeneral Requirements of Financial Statements5 minAlternative Financial Reporting systems5 min
- 3. Understanding the Income Statement13 Lessons 96 MinThis section of the financial reporting course is dedicated to the Income Statement. We explore and give examples of the main Income Statement items—gross and net revenue, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), Selling, General and Administrative expenses (SG&A), payroll expenses, interest, taxes, and others. We show you how to calculate different levels of profitability, Earnings per Share (EPS), and Diluted Earnings per Share (DEPS). Last but not least, we examine the items that are included in the Other Comprehensive Income section.Components of the Income Statement9 minAlternative Presentation Formats4 minRevenue Recognition - Principles10 minRevenue Recognition - Practical Applications6 minExpense Recognition - Principles5 minExpense recognition - Practical Applications11 minFinancial Reporting for Non-recurring Items9 minOperating and Non- operating Components of the Income Statement3 minEarnings per Share (EPS)11 minDilutive vs. Antidilutive Securities14 minCommon-size Income Statement4 minThe Income Statement - Ratio Analysis5 minWhat is Other Comprehensive Income5 min
- 4. Understanding the Balance Sheet12 Lessons 88 MinHere, we cover in detail the main Balance Sheet elements - current and non-current assets and liabilities and shareholders’ equity. We explore different measurement bases of these elements (historical cost, current cost, fair value, etc.) and explain what a Common-Size Balance Sheet is. Lastly, we calculate and interpret some liquidity and solvency ratios.Components of the Balance Sheet6 minThe Balance Sheet - Alternative Presentation Formats3 minMajor Uses and Limitations of Balance Sheet5 minCurrent Assets12 minNon-current Assets11 minCurrent Liabilities9 minNon-current Liabilities5 minMeasurement Bases8 minShareholders' Equity8 minCommon-size Balance Sheet4 minLiquidity Ratios10 minSolvency Ratios7 min
- 5. Understanding the Cash Flow Statement13 Lessons 67 MinThis section of the financial reporting course is dedicated to the specifics of the Cash Flow Statement. You will learn how to prepare a Cash Flow Statement using the direct and indirect methods and how to convert from one to the other. We also show you what a Common-Size Cash Flow Statement looks like and how to calculate the Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), Free Cash Flow to Equity (FCFE), and other cash flow ratios.Introduction to Cash Flow Statements5 minMajor Sections in the Cash Flow Statement6 minHow to Treat Non-cash Items2 minIFRS vs. US GAAP - Cash Flow3 minDirect vs. Indirect Method5 minHow is the Cash Flow Statement Linked to Other Financial Statements3 minConstructing an Indirect Cash Flow Statement11 minConstructing a Direct Cash Flow Statement3 minConverting from the Indirect to Direct Method5 minCash Flows from Investing and Financing activities6 minCommon-size Cash Flow Statement4 minFree Cash Flow Indicators7 minCash Flow Ratios7 min
- 6. The Importance of Financial Reporting Quality9 Lessons 43 MinKnowing the main elements in the core financial statements gives you a broader perspective of financial reporting. In this section of The Fundamentals of Financial Reporting course, we define the “quality” of financial reporting and introduce a spectrum for assessing it. Some of the other topics we cover in this section include Conservative vs. Aggressive accounting practices, the Fraud Triangle, and the typical accounting warning signs.What is Financial Reporting Quality3 minSpectrum for Assessing Financial Reporting Quality4 minConservative vs. Aggressive Accounting5 minMotivations for Low-quality Financial Reporting4 minThe Fraud Triangle3 minMechanisms that Discipline Financial Reporting Quality5 minPresentation Choices4 minManipulations of Financial Results7 minAccounting Warning Signs8 min
Topics
Course Requirements
- Highly recommended to take the Accounting and Financial Statement Analysis course first
Who Should Take This Course?
Level of difficulty: Beginner
- Aspiring accountants, financial controllers, financial analysts
- Everyone who wants to work in finance
Exams and Certification
A 365 Financial Analyst Course Certificate is an excellent addition to your LinkedIn profile—demonstrating your expertise and willingness to go the extra mile to accomplish your goals.
Meet Your Instructor
Antoniya is a finance professional with vast experience in accounting, auditing, financial management, and multiple high-level finance roles. She holds two master’s degrees—in Finance and in Contemporary Educational Technologies. She has worked as an auditor at PwC, as a financial controller at Atos, as an FP&A Manager and Senior Manager at Coca-Cola, and currently, as a Finance Manager at 365. Her passion for finance and teaching brought her to the 365 Тeam. She has been tutoring on various topics, including accounting, financial reporting, financial planning and analysis, economics, etc. Antoniya’s qualifications and engaging teaching style make the learning process enjoyable, and her courses have helped numerous students progress in their careers.
What Our Learners Say
365 Financial Analyst Is Featured at
Our top-rated courses are trusted by business worldwide.
