Market Regulation Objectives
This guide explores the core objectives of market regulation, from preventing fraud and insider trading to reducing default risk. It highlights how effective regulation fosters transparency, investor protection, and economic stability.
Join over 2 million professionals who advanced their finance careers with 365. Learn from instructors who have worked at Morgan Stanley, HSBC, PwC, and Coca-Cola and master accounting, financial analysis, investment banking, financial modeling, and more.
Start for FreeMarket regulation has existed since ancient civilizations first imposed penalties for theft and fraud, recognizing the need to maintain fairness and order. While society has evolved dramatically since then, the fundamental purpose of market regulation remains consistent: ensuring market integrity, protecting investors, and fostering economic stability. This text explores market regulation’s main objectives and mechanisms—highlighting its essential role in the contemporary financial system.
Prevention of Fraud and Theft
One primary objective of market regulation is preventing fraud and theft. In financial markets, complexity often translates to greater opportunities for misconduct. Investment managers and brokers frequently possess significantly more information than their less-informed clients, creating information asymmetry that can lead to exploitation. Distinguishing genuine skill from mere luck becomes increasingly challenging, especially when financial outcomes are unpredictable.
To counteract this, regulators establish minimum competence standards and performance evaluation guidelines. Prominent examples include the CFA Program and the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS), which are designed to enhance transparency and accountability. Regulators also protect unsophisticated investors by ensuring trades match their risk profiles.
Enhancing Information Transparency
Information asymmetry can significantly hinder market efficiency. If data access is costly or complicated, investors trade less frequently, and markets become inefficient. Regulatory bodies—such as the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and the US Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)—have addressed this issue by mandating standardized financial reporting practices. Companies adhering to these standards typically attract more investors, enhancing their valuation compared to firms not complying.
Ensuring Fair Trading Practices
Another critical regulatory goal is preventing insider trading. Insider trading occurs when corporate insiders or informed traders exploit exclusive, confidential information for personal gain—creating an unfair advantage. To combat this, regulatory bodies worldwide have classified insider trading as illegal, aiming to uphold investor confidence. Without such enforcement, investors might withdraw from markets they perceive as rigged, thereby reducing overall market liquidity and efficiency.
Reducing Default Risk
Market regulation also seeks to mitigate default risks. In unregulated markets, participants are often less inclined to honor financial commitments—imposing significant costs on counterparties and potentially destabilizing the entire financial system. Regulators address this by setting minimum capital requirements for companies. These regulations ensure organizations can fulfill long-term obligations and encourage prudent risk management—particularly critical for institutions like insurance companies and pension funds, whose decisions significantly impact individual financial security.
Regulators and Their Roles
Market oversight typically involves governmental agencies and self-regulatory organizations (SROs). Entities like stock exchanges and clearinghouses often possess regulatory authority to govern their members, though under strict governmental oversight. In the US, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) supervises and regulates market activities to ensure compliance with established standards and practices.
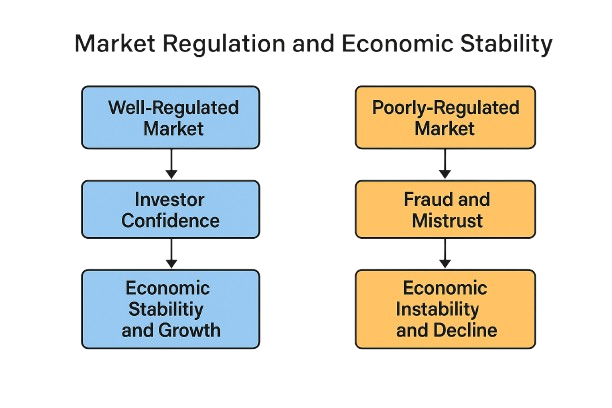
The Vital Role of Effective Market Regulation
Effective market regulation is crucial for economic health and stability. Insufficient regulation leads to increased fraud, market inefficiencies, reduced investor confidence, and potentially severe economic downturns. When regulators effectively address issues like fraud, insider trading, information asymmetry, and default risk, they create an environment conducive to fair competition, robust investor protection, and sustained economic growth. Ultimately, the enduring lesson remains clear: honesty and transparency continue to be indispensable in maintaining healthy and prosperous financial markets.
To deepen your understanding of these principles and build real-world financial skills, join the 365 Financial Analyst platform today.
